Which Of The Following Industries Has The Primary Goal Of Creating A Desire For Goods And Services
What is globalization?
Globalization is the process past which ideas, knowledge, data, appurtenances and services spread effectually the earth. In business, the term is used in an economic context to describe integrated economies marked by free trade, the costless menstruum of capital amidst countries and like shooting fish in a barrel access to foreign resources, including labor markets, to maximize returns and benefit for the mutual good.
Globalization, or globalisation as it is known in some parts of the world, is driven past the convergence of cultural and economic systems. This convergence promotes -- and in some cases necessitates -- increased interaction, integration and interdependence among nations. The more countries and regions of the world become intertwined politically, culturally and economically, the more globalized the earth becomes.
How globalization works
In a globalized economy, countries specialize in the products and services they accept a competitive reward in. This generally ways what they can produce and provide most efficiently, with the least amount of resources, at a lower cost than competing nations. If all countries are specializing in what they do best, production should be more than efficient worldwide, prices should be lower, economical growth widespread and all countries should benefit -- in theory.
Policies that promote free trade, open borders and international cooperation all drive economic globalization. They enable businesses to admission lower priced raw materials and parts, take advantage of lower cost labor markets and access larger and growing markets effectually the earth in which to sell their goods and services.
Money, products, materials, data and people menstruation more swiftly across national boundaries today than ever. Advances in applied science take enabled and accelerated this flow and the resulting international interactions and dependencies. These technological advances have been especially pronounced in transportation and telecommunications.
Amidst the contempo technological changes that have played a role in globalization are the following:
Internet and cyberspace communication. The internet has increased the sharing and flow of data and knowledge, access to ideas and exchange of culture amid people of unlike countries. Information technology has contributed to closing the digital divide betwixt more than and less advanced countries.
Communication engineering science. The introduction of 4G and 5G technologies has dramatically increased the speed and responsiveness of mobile and wireless networks.

IoT and AI. These technologies are enabling the tracking of assets in transit and as they move beyond borders, making cross-border product direction more efficient.
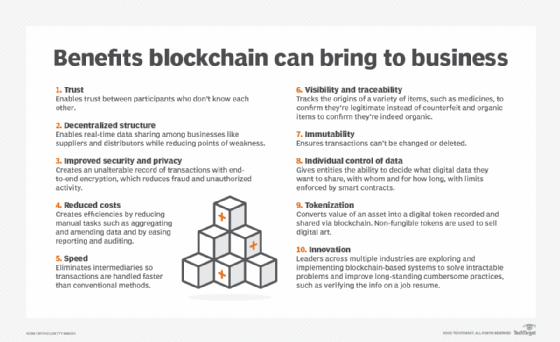
Blockchain. This engineering is enabling the development of decentralized databases and storage that support the tracking of materials in the supply chain. Blockchain facilitates the secure access to data required in industries such every bit healthcare and cyberbanking. For example, blockchain provides a transparent ledger that centrally records and vets transactions in a manner that prevents corruption and breaches.
Transportation. Advances in air and fast track engineering accept facilitated the motility of people and products. And changes in shipping logistics applied science moves raw materials, parts and finished products around the globe more efficiently.
Manufacturing. Advances such equally automation and 3D printing take reduced geographic constraints in the manufacturing industry. 3D printing enables digital designs to exist sent anywhere and physically printed, making distributed, smaller-scale production near the point of consumption easier. Automation speeds up processes and supply chains, giving workforces more flexibility and improving output.
Why is globalization important?
Globalization changes the way nations, businesses and people collaborate. Specifically, information technology changes the nature of economic activity amidst nations, expanding trade, opening global supply chains and providing admission to natural resources and labor markets.
Changing the manner trade and financial exchange and interaction occurs amongst nations likewise promotes the cultural exchange of ideas. It removes the barriers set by geographic constraints, political boundaries and political economies.
For case, globalization enables businesses in one nation to access another nation'south resources. More than open access changes the way products are developed, supply chains are managed and organizations communicate. Businesses find cheaper raw materials and parts, less expensive or more skilled labor and more efficient ways to develop products.
With fewer restrictions on trade, globalization creates opportunities to aggrandize. Increased trade promotes international contest. This, in turn, spurs innovation and, in some cases, the exchange of ideas and knowhow. In add-on, people coming from other nations to do business concern and piece of work bring with them their own cultures, which influence and mix with other cultures.
The many types of exchange that globalization facilitates tin can have positive and negative effects. For instance, the exchange of people and goods across borders can bring fresh ideas and assist concern. All the same, this movement tin can as well heighten the spread of affliction and promote ideas that might destabilize political economies.
History of globalization
Although many people consider globalization a twentieth century phenomenon, the process has been happening for millennia. Examples include the following:
- The Roman Empire. Going back to 600 B.C., the Roman Empire spread its economic and governing systems through significant portions of the ancient world for centuries.
- Silk Route trade. These trade routes, which date from 130 B.C. to 1453 A.D., represented another wave of globalization. They brought merchants, goods and travelers from Mainland china through Central Asia and the Middle East to Europe.
- Pre-World State of war I. European countries fabricated significant investments overseas in the decades earlier World State of war I. The period from 1870 to 1914 is called the golden age of globalization.
- Mail-World State of war 2. The United States led the effort to create a global economical system with a set of broadly accustomed international rules. Multinational institutions were established such as the United Nations (United nations), International Monetary Fund, World Bank and World Trade Organisation to promote international cooperation and free trade.
The term globalization as it'southward used today came to prominence in the 1980s, reflecting several technological advancements that increased international interactions. IBM's introduction of the personal computer in 1981 and the subsequent evolution of the modern internet are two examples of technology that helped drive international communication, commerce and globalization.
Globalization has ebbed and flowed throughout history, with periods of expansion and retrenchment. The 21st century has witnessed both. Global stock markets plummeted subsequently the Sept. xi, 2001, terrorist attacks in the United states of america, just rebounded in subsequent years.
More recently, nationalist political movements accept slowed clearing, closed borders and increased trade protectionism. The pandemic has had similar effects on borders and clearing and also disrupted supply chains. Notwithstanding, overall, the early 21st century has seen a dramatic increase in the stride of global integration. Rapid advances in technology and telecommunications are responsible for much of this change.
What is the G20?
The G20, or Grouping of 20, is an international forum that aims to foster international cooperation past addressing global economic issues, such as fiscal stability and climatic change. The G20 is made upwardly of 19 countries and the European Union, including nigh of the world's largest economies.
The nations involved account for 60% of the planet's population, 75% of global merchandise and 80% of world GDP. Information technology was founded in 1999, following the 1997 financial crisis, and has met every year since then.
Since 2008, the G20 has held an almanac summit that brings together heads of country to discuss of import economical issues. The G20's president is selected annually on a rotating basis, and that person'southward home country hosts the summit.
In 2019, the top was held in Osaka, Nippon, and it addressed issues such every bit women'south empowerment, climatic change and artificial intelligence. The 2020 superlative was to be in Riyadh, Saudi arabia, just was held virtually because of the pandemic. 3 of the main themes addressed were empowering people, especially women and youth; safeguarding the planet; and long-term strategies to share the benefits of innovation and technological advancement. The 2021 summit will exist held in Rome, Italy, and will focus on recovery from the pandemic and climate change.
The members of G20 are Argentine republic, Australia, Brazil, Canada, Communist china, French republic, Germany, Nippon, India, Republic of indonesia, Italy, United mexican states, Russia, S Africa, Saudi Arabia, South Korea, Turkey, the United Kingdom, the United States and the European Union. Spain is a permanent invitee of the organization.
Types of globalization: Economic, political, cultural
There are three types of globalization.
- Economic globalization. Here, the focus is on the integration of international financial markets and the coordination of financial exchange. Free trade agreements, such the North American Gratis Merchandise Agreement and the Trans-Pacific Partnership are examples of economic globalization. Multinational corporations, which operate in ii or more than countries, play a large part in economic globalization.
- Political globalization. This type covers the national policies that bring countries together politically, economically and culturally. Organizations such as NATO and the United nations are function of the political globalization endeavour.
- Cultural globalization. This aspect of globalization focuses in a large part on the technological and societal factors that are causing cultures to converge. These include increased ease of advice, the pervasiveness of social media and admission to faster and better transportation.
These three types influence ane some other. For example, liberalized national trade policies drive economic globalization. Political policies also affect cultural globalization, enabling people to communicate and motility around the globe more freely. Economic globalization besides affects cultural globalization through the import of goods and services that betrayal people to other cultures.
Effects of globalization
The effects of globalization can be felt locally and globally, touching the lives of individuals as well as the broader order in the post-obit ways:
- Individuals. Hither, a diverseness of international influences touch ordinary people. Globalization affects their access to goods, the prices they pay and their ability to travel to or fifty-fifty move to other countries.
- Communities. This level encompasses the affect of globalization on local or regional organizations, businesses and economies. It affects who lives in communities, where they work, who they piece of work for, their power to move out of their community and into one in some other country, amidst other things. Globalization as well changes the way local cultures develop within communities.
- Institutions. Multinational corporations, national governments and other organizations such equally colleges and universities are all affected past their country's approach to and credence of globalization. Globalization affects the ability of companies to grow and aggrandize, a university's power to diversify and grow its student trunk and a government'south power to pursue specific economic policies.
While the effects of globalization can be observed, analyzing the internet touch is more circuitous. Proponents often see specific results as positive and critics of globalization view the aforementioned results as negative. A human relationship that benefits i entity may damage another, and whether globalization benefits the world at big remains a betoken of contention.
Examples of globalization
Multinational corporations are a tangible example of globalization. Some examples include the following:
- McDonald's had 39,198 fast-food restaurants in 119 countries and territories, according to its Securities and Exchange Commission filing at the cease of 2020. Information technology employed more than two.two 1000000 people at that time, the filing said.
- Ford Motor Company reported in 2021 that it works with about one,200 tier 1 suppliers around the globe.
- Amazon's recent expansion has it using tens of thousands of suppliers and employing more than nearly 1.3 meg full- and part-time employees.
Through their influence on social and economical development in the countries that host them, multinational corporations embody the contradictions of globalization. They bring jobs, skills and wealth to the region they are investing or doing business in. But they too can destroy local businesses, exploit inexpensive labor and threaten indigenous cultures. The benefits they offering are often unsustainable because the loyalty of multinationals is to their investors and lesser lines and non to the local people, economies and cultures where they are doing business.
Another example of globalization is the response to the COVID-nineteen pandemic. Considering the globe was able to communicate across boundaries, nations were able to work together to rapidly produce vaccines for the virus. In addition, doctors traveled where they were needed. For case, Republic of cuba sent doctors to Italian republic at the kickoff of the pandemic to assist with the crisis equally it developed there.
Notwithstanding, countries too enacted strict travel restrictions and many closed their borders to cut down on the free movement of people and spread of the virus.
Benefits of globalization
Globalization enables countries to admission less expensive natural resources and lower cost labor. Equally a result, they can produce lower cost goods that can be sold globally. Proponents of globalization fence that information technology improves the state of the earth in many ways, such as the following:
- Solves economic problems. Globalization moves jobs and capital to places that need these resource. It gives rich countries access to lower cost resources and labor and poorer countries access to jobs and the investment funds they need for development.
- Promotes complimentary trade. Globalization puts pressure on nations to reduce tariffs, subsidies and other barriers to gratuitous merchandise. This consequently promotes economic growth, creates jobs, makes companies more competitive and lowers prices for consumers.
- Spurs economic development. Theoretically, globalization gives poorer countries access to foreign capital and engineering science they would not otherwise take. Foreign investment tin issue in an improved standard of living for the citizens of those nations.
- Encourages positive trends in human rights and the environment. Advocates of globalization indicate to improved attending to human being rights on a global scale and a shared understanding of the touch of people and product on the environment.
- Promotes shared cultural agreement. Advocates view the increased ability to travel and feel new cultures equally a positive office of globalization that can contribute to international cooperation and peace.
Negative consequences of globalization
Many proponents view globalization as manner to solve systemic economic bug. Just critics run across it as increasing global inequality. Among the critiques of globalization are the following problems:
- Destabilizes markets. Critics of globalization blame the elimination of trade barriers and the freer move of people for undermining national policies and local cultures. Labor markets in particular are affected when people movement across borders in search of higher paying jobs or companies outsource piece of work and jobs to lower cost labor markets.
- Damages the environment. The transport of appurtenances and people among nations generates greenhouse gas and all the negative effects it has on the environment. Global travel and trade also can introduce, sometimes inadvertently, invasive species to foreign ecosystems. Industries such equally angling and logging tend to go where business is most lucrative or regulations are less strict, which has resulted in overfishing and deforestation in some parts of the earth.
- Lowers living standards. When companies move operations overseas to minimize costs, such moves can eliminate jobs and increase unemployment in sectors of the home state.
- Facilitates global recessions. Tightly integrated global markets behave a greater chance of global recessions. The 2007-2009 financial crisis and Great Recession is a good example of how intertwined global markets are and how financial issues in one country or region tin quickly affect other parts of the world. Globalization reduces the ability of individual nations to effectively use monetary and fiscal policy to control the national economic system.
- Damages cultural identities. Critics of globalization decry the decimation of unique cultural identities and languages that comes with the international movement of businesses and people. At the same time, the net and social media are driving this trend even without the movement of people and commerce.
- Increases the likelihood of pandemics. Increased travel, critics say, has the potential to increment the take a chance of pandemics. The H1N1 (swine flu) outbreak of 2009 and coronavirus in 2020 and 2021 are two examples of serious diseases that spread to multiple nations quickly.
Time to come of globalization
Technological advances, particularly blockchain, mobile communication and cyberbanking, are fueling economic globalization.
Nonetheless, rising levels of protectionism and anti-globalization sentiment in several countries could slow or even reverse the rapid pace of globalization. Nationalism and increasing trends toward conservative economic policies are driving these anti-globalization efforts.
Global trade is also made more hard and facing ascent threats from other factors, such as these:
- climate change
- decaying infrastructure
- cyber attacks
- homo rights abuses
The takeaway
Globalization is a longstanding trend that is in the process of changing and possibly slowing. There are advantages to the more open border and complimentary trade that globalization promotes, also as negative consequences.
In a modernistic, post-pandemic world, individuals, businesses and countries must consider both sides of the globalization issue. Learn how companies are rethinking global supply bondage to avoid disruption and reap the benefits of globalization.
Which Of The Following Industries Has The Primary Goal Of Creating A Desire For Goods And Services,
Source: https://www.techtarget.com/searchcio/definition/globalization
Posted by: mcpeekhurse1984.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Which Of The Following Industries Has The Primary Goal Of Creating A Desire For Goods And Services"
Post a Comment